Comparison and Analysis of HDMI and Optical Cables
Introduction
In modern home audiovisual systems, the choice of audio connection method directly impacts the viewing and listening experience. Currently, HDMI cables and optical cables are the two most common digital audio transmission methods. Selecting the appropriate audio connection method is crucial for the audiovisual experience. The right connection not only ensures high-fidelity sound quality but also enhances system compatibility and ease of use, thereby improving the overall entertainment experience.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison and analysis of HDMI and optical audio cables in terms of sound quality, compatibility, ease of use, and other aspects, helping readers make the best choice based on their individual needs.

Basic Concepts
HDMI Cables
HDMI, short for High Definition Multimedia Interface, is a cable standard used for transmitting digital audio and video signals. This type of cable can simultaneously transmit high-quality video and multi-channel audio signals, widely used in televisions, projectors, game consoles, and home theater systems.
Key Features
- Supports various audio formats, such as Dolby TrueHD, Dolby Atmos, DTS HD Master Audio.
- Supports high-resolution video transmission, including 4K, 8K, and High Dynamic Range (HDR) videos.
- Equipped with CEC (Consumer Electronics Control) functionality, allowing control of multiple devices with a single remote.

Optical Cables
Optical cables, typically referring to fiber optic audio cables like Toslink or S/PDIF, use light signals to transmit data and are specifically designed for digital audio signal transmission. Optical cables primarily transmit high-quality digital audio signals, commonly used to connect televisions, sound systems, and game consoles.
Key Features
- Resistant to electromagnetic interference, ensuring the purity of the audio signal.
- Suitable for long-distance transmission with minimal signal attenuation.

Main Differences Between HDMI and Optical Cables
Transmission Capabilities
Audio
- HDMI: Supports high-resolution, multi-channel audio formats such as Dolby TrueHD, Dolby Atmos, DTS HD Master Audio, suitable for high-end sound systems.
- Optical: Supports limited audio formats and channels, mainly including Dolby Digital and DTS, with a maximum of 5.1-channel surround audio.
Video
- HDMI: Capable of transmitting high-quality video and audio signals simultaneously, reducing the number of cables and simplifying connections.
- Optical: Only supports audio transmission, requiring additional video connection cables like HDMI or other video transmission methods, increasing cabling complexity.
Transmission Distance
- HDMI: Optimal transmission distance is typically within 5 meters. For longer distances, high-quality or active HDMI cables are recommended to ensure signal stability.
- Optical: Recommended length is 10 meters, extendable up to 30 meters with minimal signal attenuation, suitable for long-distance audio transmission needs.
Interference Resistance
- HDMI: Composed of copper wires, it may be susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI), especially in environments with complex electromagnetic conditions.
- Optical: Made of glass fibers, completely resistant to electromagnetic interference, ensuring pure audio signal transmission.
Comparison Table
Below is a concise comparison table outlining the main differences between HDMI and Optical cables, focusing on Transmission Capabilities (Audio and Video), Transmission Distance, and Interference Resistance.
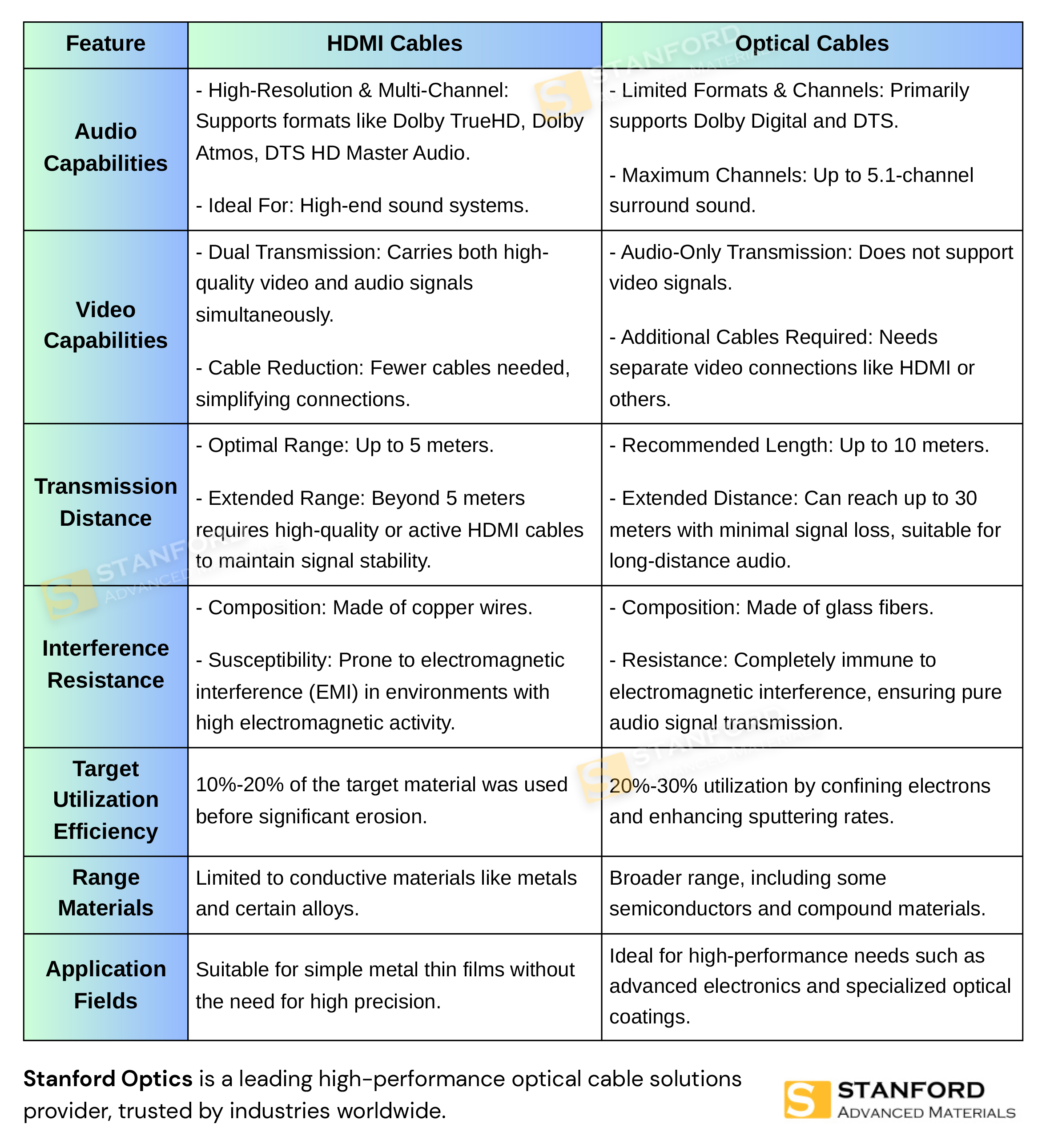
Detailed Comparison Between HDMI ARC and Optical Audio Cables
HDMI ARC (Audio Return Channel)
HDMI ARC enables bidirectional audio transmission between devices using a single HDMI cable, simplifying connections and reducing the number of cables required.
Supports audio and video bidirectional transmission, allowing the television to send audio signals to speakers or AV receivers while receiving audio signals from these devices.
Advantages
- Supports More Audio Formats and Channels: Includes high-quality audio formats like Dolby TrueHD and Dolby Atmos.
- Equipped with CEC Functionality: Enables control of multiple devices with a single remote, making operations more convenient.
- Reduces Cable Count: Only one HDMI cable is needed to transmit audio and video signals, enhancing neatness.
Disadvantages
- Compatibility Issues: Depends on devices supporting the same HDMI version, which may lead to compatibility problems.
- Higher Cost: Active HDMI cables may require additional power, increasing costs.
Optical Audio Cables
Optical audio cables transmit audio data through light signals and are widely used for connecting audio equipment.
Only transmits audio signals, suitable for devices without HDMI ports, such as some older models of televisions and sound systems.
Advantages
- Electromagnetic Interference Resistance: Suitable for long-distance transmission, ensuring the purity of audio signals.
- Better Compatibility: Suitable for older devices with widespread interface availability.
- Easy Installation and Use: Does not require complex configurations, making it user-friendly.
Disadvantages
- Limited Audio Formats: Only supports limited audio formats and channels, unable to meet high-end audio requirements.
- Requires Additional Cables for Video Transmission: Increases cabling complexity and the number of cables.
- Does Not Support the Latest High-Resolution Audio Formats: Unable to transmit lossless audio formats like Dolby Atmos.
Audio Quality Transmission Comparison
Supported Audio Formats
HDMI ARC/eARC
Supports high-quality audio formats such as Dolby TrueHD, Dolby Atmos, DTS-HD Master Audio, suitable for multi-channel surround sound, providing an immersive auditory experience.
Optical
Only supports lossy audio formats like Dolby Digital and DTS, lacking support for lossless formats like Dolby Atmos, resulting in slightly inferior sound quality.
Number of Channels
HDMI ARC
Supports up to 32-channel PCM audio, catering to complex multi-channel audio needs, ideal for high-end home theater systems.
Optical
Supports up to 5.1-channel surround audio, suitable for mid to low-end sound systems, unable to meet higher-level audio demands.
Other Audio Quality Factors
- Lossless vs. Lossy Audio Transmission: HDMI ARC supports lossless audio transmission, ensuring high-fidelity sound quality; optical primarily transmits lossy audio, resulting in some sound quality loss.
- Signal Integrity and Latency: HDMI ARC has lower transmission latency, suitable for audiovisual equipment requiring high synchronization; optical maintains high signal integrity but may experience synchronization issues when connecting multiple devices.
Compatibility and Device Support
Device Compatibility
HDMI ARC
Requires devices to support HDMI ARC or eARC functionality. Most modern televisions, sound systems, and AV receivers are equipped with this feature, ensuring good compatibility.
Optical
Suitable for devices with optical ports, including older televisions, sound systems, and audio equipment, offering broad compatibility.
Future Compatibility
- HDMI: Standards are continually upgraded (such as HDMI 2.1 and eARC), supporting higher quality audio and video transmission, offering stronger future adaptability.
- Optical: Limited support for future new audio formats, struggling to meet the rapid development of audio technology demands.
Ease of Use and Installation
Connection and Setup
HDMI ARC
Simple to connect, requiring only one HDMI cable to transmit audio and video. Supports CEC functionality, allowing control of multiple devices with a single remote, making operations more convenient.
Optical
Only transmits audio signals, requiring additional video connection cables (like HDMI or other video transmission methods), increasing cabling complexity. Some devices may require manual configuration of audio output settings, making usage slightly cumbersome.
Cable Management
HDMI ARC
Reduces the number of cables, resulting in cleaner wiring and contributing to a tidy audiovisual environment.
Optical
Requires additional video cables, which may lead to tangled cables, affecting aesthetics and user experience.
Real-world application Cases and User Feedback
Application in Different Home Theater Systems
High-End Home Theaters
High-end home theater systems typically prioritize HDMI ARC/eARC to support the latest audio formats and multi-channel audio, providing top-tier viewing and listening experiences.
Mid to Low-End Systems or Older Devices
For mid to low-end sound systems or users with older equipment, optical cables remain a practical choice as an auxiliary audio transmission method, meeting basic audio transmission needs.
Actual User Feedback
Users generally find HDMI ARC/eARC to excel in sound quality and ease of use, making it suitable for those seeking high-quality audiovisual experiences. Meanwhile, optical cables are favored by users with older equipment or limited budgets due to their good compatibility and resistance to interference.
Common Issues and Solutions
- Compatibility Problems: Ensure all devices support the same HDMI version. If necessary, upgrade firmware or replace cables with ones supporting the required features.
- Audio Latency: Check device settings, adjust audio synchronization options, or use cables and devices that support low latency.
- Cable Length Limitations: Choose cables of appropriate lengths based on actual needs. For long-distance transmission, high-quality or active HDMI cables are recommended, while optical cables are better suited for long distances.
Selection Guide
Checking Device Compatibility
Before choosing a connection method, confirm whether your devices support HDMI ARC/eARC or have optical ports. Additionally, understand the supported audio formats and number of channels to ensure optimal compatibility.
Audio Requirements
- High-Resolution, Multi-Channel Audio: Prefer HDMI ARC/eARC for lossless sound quality and multi-channel support.
- Basic Audio Needs or Older Devices: Optical cables are a cost-effective option, fulfilling basic audio transmission requirements.
Transmission Distance and Environment
- Short Distance, High-Quality Transmission: Choose HDMI cables to ensure high-fidelity audio and video signal transmission.
- Long Distance, Interference Resistance: Optical cables are more suitable, ensuring stable signals unaffected by electromagnetic interference.
Budget and Installation Complexity
- Simplified Connections and Control: Choose HDMI ARC/eARC to reduce the number of cables and complexity, enhancing neatness.
- Cost-Sensitive and No Need for High-End Audio: Optical cables are more economical, suitable for users with limited budgets and no requirement for advanced audio formats.
Conclusion
HDMI and optical audio cables each have their advantages and disadvantages, suitable for different usage scenarios and needs. HDMI ARC/eARC performs exceptionally well in modern home theater systems, supporting higher-quality audio and video transmission with strong compatibility. On the other hand, optical cables, with their resistance to interference and broad device compatibility, are ideal for specific scenarios and older equipment.
When choosing an audio connection method, consider factors such as device compatibility, audio quality requirements, transmission distance, and budget. For users pursuing a comprehensive audiovisual experience, prioritize HDMI ARC/eARC. For those with specific needs or older equipment, optical cables offer a practical and economical alternative.
By weighing the above factors, you can select the most suitable audio connection method based on your actual situation, enhancing the overall performance of your home audiovisual system.
About Stanford Optics
Stanford Optics is a leading high-performance optical cable solutions provider, trusted by industries worldwide. Focusing on quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction, we specialize in delivering tailored fiber optic products designed to meet the diverse needs of modern communication and infrastructure projects.
For more information about our products and services, please visit our product category.




