A Comprehensive Comparison of DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5
Introduction
Server Random Access Memory (RAM) is a critical component in network servers, directly influencing performance, reliability, and scalability. As technology advances, selecting the appropriate DDR (Double Data Rate) memory becomes increasingly complex. Understanding the differences between DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5 is essential for optimizing server operations and ensuring future-proofing investments.
Source: Martini, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
DDR Technology Overview
DDR memory transfers data on the rising and falling edges of the clock signal, effectively doubling the data rate without increasing the clock frequency. Since its inception, DDR technology has evolved through several generations, each enhancing performance, power efficiency, and capacity. This evolution—from DDR1 to DDR5—reflects the growing demands of modern computing environments.
Generations of DDR Memory
DDR3 (Released in 2007)
DDR3 memory builds upon DDR2 by doubling data transfer speeds, offering:
- Frequency Range: 400-1067 MHz
- Voltage: 1.5V
- Maximum DIMM Capacity: 16GB
- Compatibility: Suitable for platforms like Intel LGA1366 to LGA1151 and AMD AM3/AM3+/FM1/2/2+
DDR3 improved bandwidth and reduced power consumption compared to its predecessor, making it a popular choice for servers requiring reliable performance at a lower cost.
DDR4 (Released in 2014)
DDR4 introduced significant enhancements over DDR3:
- Increased Module Density: Higher capacity DIMMs, up to 64GB per module.
- Reduced Voltage: Operating at 1.2V, DDR4 is more power-efficient.
- Enhanced Data Transfer Rates: Frequencies ranging from 800-1600 MHz.
- Market Dominance: By 2017, DDR4 became the market standard, achieving approximately 80% market share by 2020.
DDR4’s advancements support higher performance and scalability, meeting the demands of modern data centers and enterprise servers.
DDR5 (Released in 2020)
DDR5 pushes the boundaries further with:
- Higher Data Rates: Frequencies from 2400-3600 MHz, with data transfer rates up to 7200 MT/s.
- Lower Power Consumption: Operating at 1.1V, DDR5 reduces energy usage by an additional 20%.
- Advanced Technologies: Incorporates DFE (Decision Feedback Equalization) for better signal integrity.
- On-Module Power Management: Integrated PMIC (Power Management IC) enhances power control precision and signal quality.
DDR5 offers substantial performance improvements, making it ideal for high-demand applications and future-proof server architectures.
Comparing DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5
Physical Differences
- DDR4: Thicker modules with a different notch position compared to DDR3.
- DDR5: Further notch position changes and physical refinements to prevent cross-generation compatibility.
Compatibility Issues
Each DDR generation is not backward or forward compatible due to differing slot shapes and electrical requirements. This necessitates careful consideration when upgrading memory to ensure motherboard compatibility.
Technical Parameters Comparison
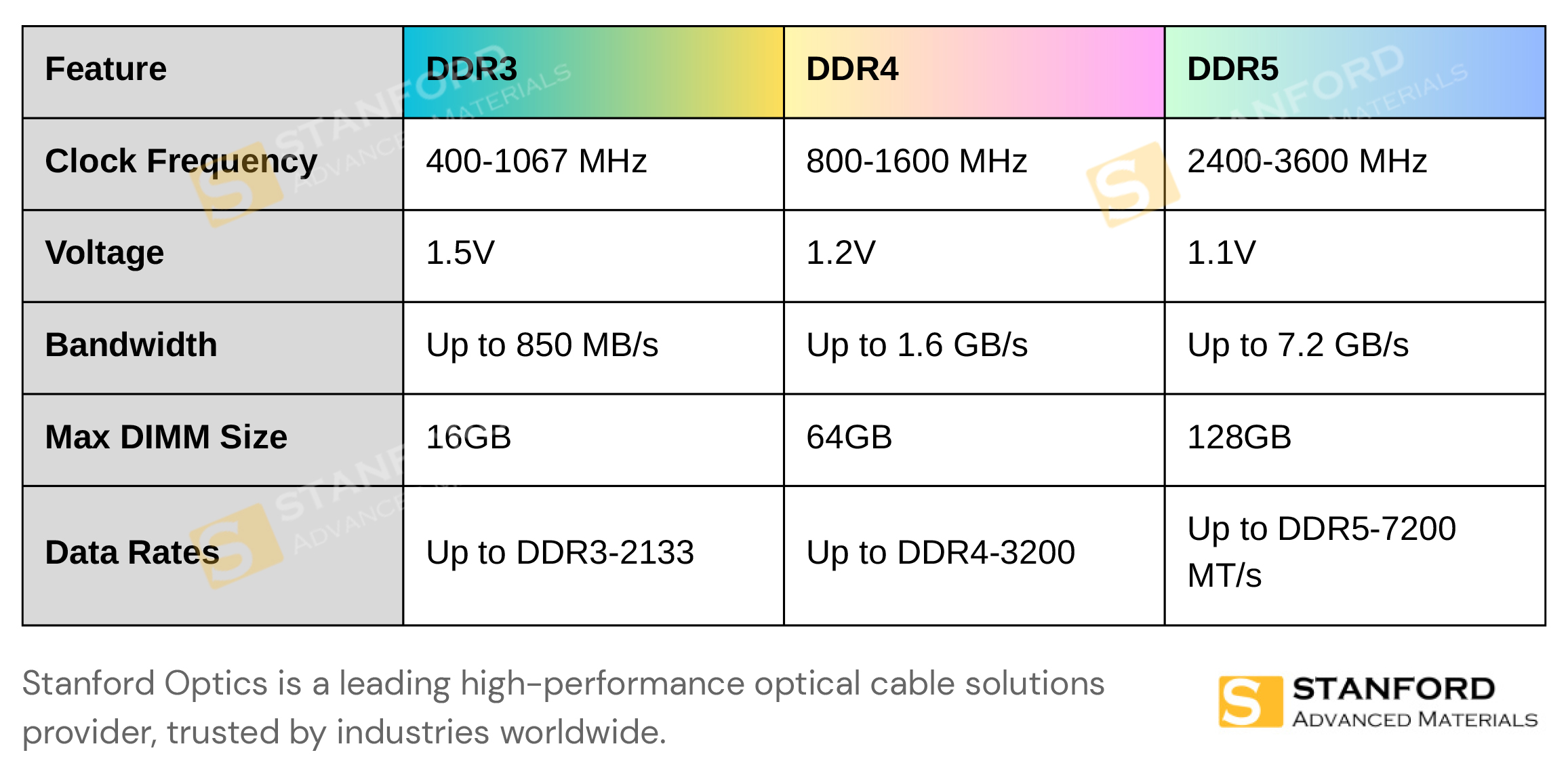
Key Differences Between DDR3 and DDR4
- Speed: DDR4 starts at 1600 MT/s, double the initial speed of DDR3.
- Power Efficiency: DDR4 operates at 1.2V, reducing power consumption by approximately 40% compared to DDR3.
- Capacity: DDR4 supports up to 512GB per module, a significant increase from DDR3’s 16GB.
- Reliability: Enhanced error detection and signal integrity technologies in DDR4 provide greater reliability for critical server applications.
Advantages of DDR5 Over DDR3 and DDR4
- Higher Starting Speed: DDR5 begins at 4800 MT/s, a 50% increase over DDR4’s 3200 MT/s.
- Lower Power Consumption: Operating at 1.1V, DDR5 offers an additional 20% reduction in power usage over DDR4.
- Built-In ECC: Integrated Error Correction Code (ECC) enhances data integrity and reduces the risk of data corruption.
- Advanced Power Architecture: On-module PMICs shift power management from the motherboard to the memory modules, improving power control accuracy and signal quality.
Is Upgrading to DDR5 Worth It?
Cost Considerations
DDR5 memory is currently more expensive than DDR4, necessitating a careful evaluation of budget constraints versus performance benefits.
Availability Issues
As of the latest updates, AMD has yet to release CPUs that fully support DDR5, with expectations tied to the launch of the Zen 4 architecture. Additionally, market supply constraints for DDR5 may affect availability and pricing.
Motherboard Compatibility
DDR5 is not compatible with DDR4 motherboards, requiring a complete system overhaul that includes a new motherboard to support the latest memory standard.
Conclusion
DDR5 RAM offers significant improvements in speed, power efficiency, and reliability over DDR4 and DDR3, positioning it as the future standard for server memory. However, upgrading to DDR5 involves higher costs, potential availability challenges, and the need for compatible motherboard infrastructure. Organizations with sufficient budgets and long-term strategic plans may find DDR5 a worthy investment, while others may continue to benefit from the robust performance of DDR4 for the time being.




