A Complete Guide to Selecting the Right Outdoor Fiber Optic Cables
1. Introduction
Choosing the right outdoor fiber optic cable is crucial to ensuring the performance and reliability of your network, especially in demanding outdoor environments. Whether you're connecting buildings on a campus, establishing a rural broadband link, or setting up an industrial network, the right cable can significantly improve signal quality, longevity, and network efficiency.
Outdoor fiber optic cables are specifically designed to withstand the harshest conditions, from extreme weather to physical stress, making them an essential part of any outdoor networking setup. With a range of cable types available, each offering unique benefits based on factors such as installation method, fiber structure, and environmental resilience, it’s important to understand how to select the right cable for your specific needs.
In this guide, we will explore the different types of outdoor fiber optic cables, explain their features, and help you make an informed choice that ensures your outdoor network is both reliable and high-performance, regardless of the conditions it faces.
2. Types of Outdoor Fiber Optic Cables
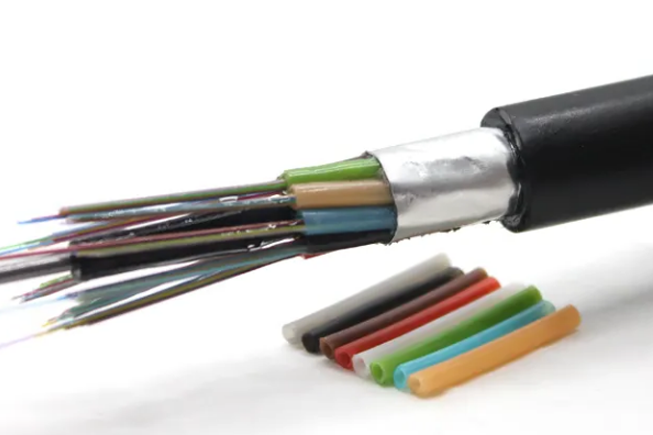
Outdoor fiber optic cables come in a variety of types, each designed to meet specific needs based on factors such as environmental conditions, installation methods, and performance requirements. Understanding the different types of outdoor fiber optic cables is essential for selecting the best option for your application. These cables are typically classified by their structure, installation methods, and core sizes.
Fiber Cables Classified by Structure
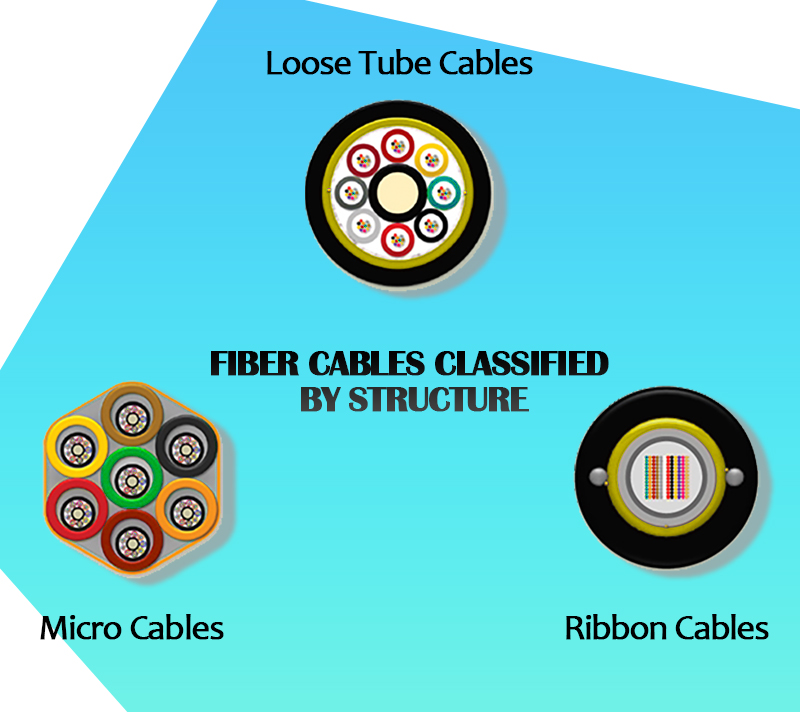
1. Loose Tube Cables
Loose tube cables are one of the most commonly used types of outdoor fiber optic cables. They are designed to protect the fibers from harsh environmental conditions. The fibers are placed within gel-filled tubes, which prevent moisture from reaching the fibers, ensuring signal stability even in wet environments. These cables can endure a wide range of temperatures, from as low as -40°C to as high as +70°C, making them ideal for areas with extreme climate conditions. Loose tube cables are highly flexible, making them perfect for high-humidity environments or outdoor installations that require flexibility and durability.
2. Micro Cables
Micro cables are ultra-compact, with diameters as small as 1-2mm. This small size allows for easy installation in congested spaces, such as within tight conduits or ducts. Micro cables provide a high fiber density, meaning that they can carry a large number of fibers in a small form factor. These cables are lightweight and highly flexible, making them ideal for environments where space is limited, such as LANs, building-to-building connections, or long-distance installations in urban areas. Although micro cables may not be as robust as loose tube cables in terms of environmental protection, they offer great efficiency in terms of fiber deployment.
3. Ribbon Cables
Ribbon cables consist of fibers that are grouped in flat, ribbon-like structures, typically in multiples of 12 or 24 fibers. This design makes it easier and faster to perform mass fusion splicing, which is beneficial for large-scale installations where many fibers need to be terminated quickly. Ribbon cables are ideal for high-density networks, as they provide a compact design that still allows for the installation of multiple fibers. The ribbon format also helps optimize space, making them a good option for both indoor and outdoor applications where high fiber counts are needed.
Fiber Cables Classified by Installation Methods
1. Aerial Cables
Aerial fiber optic cables are designed for overhead installations, typically mounted on utility poles or other elevated structures. These cables are built to withstand exposure to harsh weather conditions, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations. Aerial cables have a self-supporting design that incorporates a high-tensile strength steel messenger wire, which provides structural support and ensures stability over long distances. While slightly more expensive due to the additional materials used in their construction, aerial cables are a reliable option for telecommunications, broadband infrastructure, and small-cell installations in rural or urban environments.
2. Direct Buried Cables
Direct burial cables are ruggedly constructed to be installed directly in the ground, without the need for protective conduits. These cables feature durable jackets and additional strength members to prevent damage from physical stress, moisture, and temperature changes. They are ideal for long-distance connections, linking buildings or industrial complexes across large areas. With their ability to handle the demands of being buried, these cables are used in outdoor environments where running cables through ducts or conduits is not feasible. They provide reliable, long-term performance and are less likely to be damaged by environmental factors like flooding or extreme heat.
3. Duct Cables
Duct cables are designed for installation within underground conduits. These cables are constructed to handle the tension and abrasion associated with pulling through long conduit runs. Duct cables often feature a strong polyethylene jacket and water-blocking tape to prevent moisture from entering the cable. They are often used in environments where the cable will be subjected to physical stress but will not be directly exposed to the elements. Duct cables are versatile and provide reliable service in a variety of outdoor installations, offering a solution for networks that require underground fiber connectivity.
Fiber Cables Classified by Core Sizes
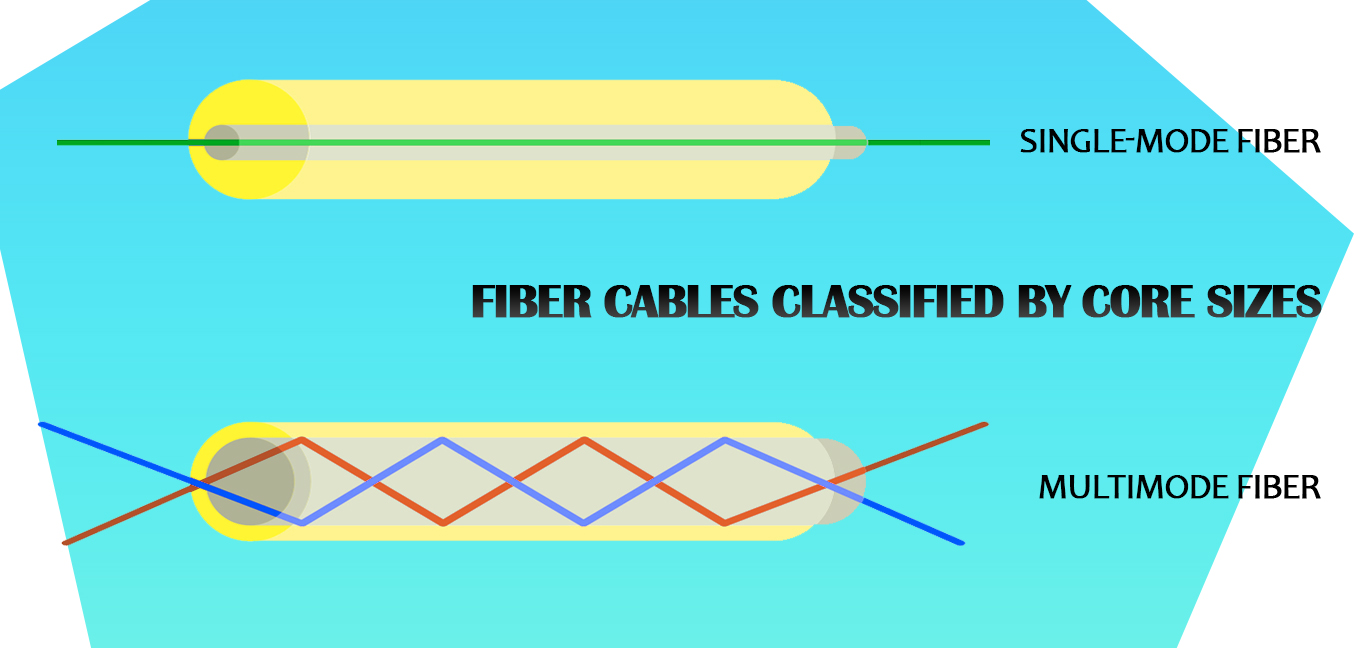
1. Outdoor Single-Mode Fiber (OS2)
Outdoor single-mode fiber optic cables have a smaller core size (around 8-10 microns) and are designed for long-distance data transmission. These fibers allow light to travel in a single path, reducing signal loss and enabling high bandwidth over great distances. They are most commonly used for backbone networks, long-haul telecommunications, and high-capacity internet connections. Outdoor single-mode fiber is the ideal choice for applications that require minimal signal attenuation and latency, making it perfect for wide-area networks (WANs) and telecommunications infrastructures.
2. Outdoor Multimode Fiber Optic Cable (OM2, OM3, OM4)
Outdoor multimode fiber optic cables have a larger core size (50-62.5 microns) and are designed for shorter-distance communication, typically within a building or a campus environment. These fibers allow light to travel along multiple paths, which can cause greater signal dispersion and loss over longer distances. However, they are still suitable for high-bandwidth applications over short distances, such as local area networks (LANs) and connections between buildings on a campus. Depending on the grade of multimode fiber (OM2, OM3, OM4), the cable can support varying data rates, with OM3 and OM4 cables supporting higher bandwidths and distances.
3. Key Considerations in Choosing Outdoor Fiber Cables
When selecting outdoor fiber optic cables, it's important to consider several factors to ensure the best performance, reliability, and future scalability. Here are the key considerations to keep in mind:
Minimal Loss and Latency
One of the most critical aspects when choosing outdoor fiber cables is minimizing signal loss and latency. Signal degradation due to fiber optic attenuation can impact network performance, especially in long-distance applications. For industries like telecommunications, data centers, and financial sectors, even the slightest delay can cause significant inefficiencies and reduce the overall quality of service.
To prevent this, loose tube cables are a popular choice for outdoor installations. These cables are designed with protective gel-filled buffer tubes, which not only safeguard fibers from physical damage but also minimize signal loss by reducing the likelihood of moisture or environmental conditions affecting the cable’s integrity. This makes them ideal for applications where data transmission over long distances is required.
For lower latency, ribbon cables can be an excellent option. Ribbon cables feature multiple fibers arranged in a flat configuration, which is well-suited for mass fusion splicing. This design minimizes the time and complexity required for fiber terminations, ensuring more efficient network operations and lower latency.
Flexibility and Scalability
In today's world, network scalability is more important than ever, as businesses and infrastructure continue to grow. As demand for high-speed internet and data services increases, the ability to expand your fiber optic network with minimal disruption becomes a critical consideration.
Loose tube cables are an ideal choice when the network needs to support moderate expansion in the future. They provide flexibility in installation, as they can be easily spliced and allow for the addition of more fibers without significant rework. For larger networks that require the installation of hundreds or thousands of fibers, ribbon cables offer greater fiber density and enable faster and more efficient upgrades, especially when the network reaches beyond 144 fibers.
Additionally, micro cables are a good option for installations in constrained spaces, allowing for easy upgrades and scalability without taking up valuable space. These cables are particularly suitable when initial fiber counts are low but need to accommodate future growth.
Emergency Recovery Performance
Outdoor fiber cables often face exposure to harsh environmental conditions, and this can sometimes result in physical damage or network outages. For example, buried cables may encounter mechanical damage due to construction activities, while aerial cables might be affected by storms or high winds.
In such situations, rapid recovery of the network is essential. Loose tube cables, although more time-consuming to repair, can identify and splice the most critical fibers based on traffic priorities. This makes them an excellent choice for networks where recovery time is not as urgent but reliability is key. On the other hand, ribbon cables offer much faster splicing times, which can be crucial for minimizing downtime in high-traffic networks. If the goal is to restore service quickly, ribbon cables are a better option due to their streamlined design and quicker recovery process.
Availability Limitations
When selecting the best fiber optic cables, it's essential to keep in mind that some cables are not universally compatible with every installation scenario. For instance, micro-loose tube cables are designed specifically for micro ducts and cannot be paired with outdoor armored cables due to size and design constraints.
Furthermore, high-performance cables may not always be suitable for all environments. For example, outdoor armored cables are designed for areas prone to physical damage and are often necessary for installations in locations where damage is more likely (such as construction zones). However, they may not be necessary in low-risk areas where standard cables can suffice, and using them might result in unnecessary costs.
It's important to carefully review the manufacturer's specifications to understand the limitations of each cable type and choose the most suitable one based on your network’s needs.
A Summary
When selecting the right outdoor fiber cable for your network, several factors need to be taken into consideration, including environmental conditions, installation methods, and future scalability. While each cable type offers specific advantages, it is essential to align the right choice with your unique needs, whether it’s ensuring minimal signal loss, accommodating future expansions, or achieving quick recovery in case of network disruptions.
To help you quickly understand the key points, the table below summarizes the most important factors and the recommended cable types for each scenario. This concise overview can serve as a handy reference for making an informed decision based on your specific requirements.
| Key Consideration | Cable Type | Main Benefit | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimal Loss and Latency | Loose Tube, Ribbon Cables | Minimize signal loss and reduce latency | Long-distance, high-demand data transmission |
| Flexibility and Scalability | Loose Tube, Ribbon Cables, Micro Cables | Scalability for future network expansion | Growing networks, high-density connections |
| Emergency Recovery Performance | Ribbon Cables, Loose Tube Cables | Faster recovery for high-traffic networks | Areas prone to physical damage or outages |
| Availability Limitations | Outdoor Armored Cables, Micro-Lose Tube | Durability in harsh environments | Construction zones, underground deployments |
By evaluating the factors in the table and understanding which type of fiber cable works best in each situation, you can make a more informed decision on the most suitable option for your outdoor network setup.
4. Conclusion
Choosing the right outdoor fiber cable depends on various factors like signal loss, latency, and installation environment. Each cable type—whether loose tube, aerial, or armored—has distinct advantages that cater to different needs. It's essential to assess these characteristics to make the best choice for your network.
For reliable and high-performance outdoor fiber optic solutions, Stanford Optics offers durable cables designed to meet the demands of harsh environments, ensuring long-term, stable network performance.